Contract No. HY/2010/02 ¡V
Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities ¡V
Reclamation Work (here below, known as ¡§the Project¡¨) mainly comprises
reclamation at the northeast
of the Hong Kong International Airport of
an area of
about 130-hectare for
the construction of an artificial island for the development of the Hong
Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities (HKBCF), and about 19-hectare for the
southern landfall of the Tuen Mun - Chek Lap Kok Link (TMCLKL). It is a
designated project and is governed by the current permits for the Project, i.e.
the amended Environmental Permits (EPs) issued on 16 Oct 2012 (EP-353/2009/E)
and 8 December 2011 (EP-354/2009/A) (for TMCLKL Southern Landfall Reclamation
only).
Ove Arup & Partners Hong
Kong Limited (Arup) was appointed by Highways Department (HyD) as the
consultants for the design and construction assignment for the Project¡¦s
reclamation works (i.e. the Engineer for the Project).
China Harbour Engineering
Company Limited (CHEC) was awarded by HyD as the Contractor to undertake the
construction work of the Project.
ENVIRON Hong Kong Ltd. was
employed by HyD as the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) and
Environmental Project Office (ENPO) for the Project.
AECOM Asia Co. Ltd. (AECOM)
was appointed by CHEC to undertake the role of Environmental Team for the
Project for carrying out the environmental monitoring and audit (EM&A)
works.
The construction phase of the
Project under the EPs was commenced on 12 March 2012 and will be tentatively
completed by early Year 2016. The EM&A programme, including air quality,
noise, water quality and dolphin monitoring and environmental site inspections,
was commenced on 12 March 2012.
This report documents the findings of EM&A
works conducted in the period between 1 and 31 January 2012. As informed by the Contractor, major activities in the
reporting period were:-
Marine-based Works
-
Laying
geo-textile
-
Maintenance
of silt curtain
-
Stone
column installation
-
Cellular
structure installation
-
Band
drain installation
Land-based Works
-
Maintenance
works of Site Office at Works Area WA2
-
Maintenance
works of Public Works Regional Laboratory at Works Area WA3
-
Sign
board erection at Works Area WA2
-
Geo-textile
fabrication at Works Area WA2
-
Stone
column installation barges setup and their maintenance works at Works Area WA4
-
Silt
curtain fabrication at Works Area WA4
A summary of monitoring and audit activities
conducted in the reporting period is listed below:
|
24-hour Total Suspended Particulates (TSP)
monitoring
1-hour TSP monitoring
|
5 sessions
5
sessions
|
|
Noise monitoring
|
5
sessions
|
|
Impact water quality monitoring
|
13 sessions
|
|
Impact dolphin monitoring
|
2 surveys
|
|
Joint Environmental site inspection
|
5 sessions
|
Breaches of Action and Limit Levels for Air
Quality
No Action/Limit Level exceedance of 1-hour TSP and 24-hour TSP results was recorded in the reporting month.
Breaches of Action and Limit Levels for
Noise
No Action/Limit Level exceedance of construction noise was recorded in the
reporting month.
Breaches of Action and Limit Levels for
Water Quality
Six (6) Action Level exceedances were recorded at measured suspended solids (SS)
values (in mg/L) in the reporting month. Investigation
result show that the exceedances were not due to the Project works.
Impact Dolphin Monitoring
A total of fifteen dolphin sightings were recorded during
the two surveys, three
on the 8 January 2013, one on the 9 January 2013 and eleven on the 28 January
2013. Of the fifteen sightings, twelve were ¡§on effort¡¨ (which are all under favourable condition) and three were ¡§opportunistic¡¨. A total of forty-six individuals were sighted from the two
impact dolphin surveys in the reporting period. Sighting details are summarised
and plotted in Appendix K and Figure 5c, respectively.
Behaviour: seven groups were feeding while none
of them were associated with a fishing vessel; three groups were recorded as travelling; three groups were associated with multiple behaviour (feeding and surface
active); one group was recorded as surface active; the behavior of
one group was unknown.
Complaint, Notification of Summons and
Successful Prosecution
As
informed by EPD on 18 January
13. One complaint was received on 18 January 13. No notification of summons and
successful prosecution was received in the reporting month.
Reporting Change
There was no reporting change required in
the reporting period.
Future Key Issues
Key issues to be considered in the coming
month included:-
-
Site
runoff should be properly collected and treated prior to discharge;
-
Minimize
loss of sediment from filling works;
-
Regular
review and maintenance of silt curtain systems, drainage systems and desilting
facilities;
-
Exposed
surfaces/soil stockpiles should be properly treated to avoid generation of
silty surface run-off during rainstorm;
-
Regular
review and maintenance of wheel washing facilities provided at all site
entrances/exits;
-
Conduct
regular inspection of various working machineries and vessels within works
areas to avoid any dark smoke emission;
-
Suppress
dust generated from work processes with use of bagged cements, earth movements,
excavation activities, exposed surfaces/soil stockpiles and haul road traffic;
-
Quieter
powered mechanical equipment should be used;
-
Provision
of proper and effective noise control measures for operating equipment and
machinery on-site, such as erection of movable noise barriers or enclosure for
noisy plants;
-
Closely
check and replace the sound insulation materials regularly;
-
Better scheduling
of construction works to minimize noise nuisance;
-
Properly
store and label oil drums and chemical containers placed on site;
-
Proper
chemicals, chemical wastes and wastes management;
-
Maintenance
works should be carried out within roofed, paved and confined areas;
-
Collection
and segregation of construction waste and general refuse on land and in the sea
should be carried out properly and regularly; and
-
Proper
protection and regular inspection of existing trees, transplanted/retained
trees.
1.1.1
Contract No. HY/2010/02 ¡V Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge
Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities ¡V Reclamation Work (here below, known as
¡§the Project¡¨) mainly comprises reclamation at the northeast of
the Hong Kong International Airport of
an area of
about 130-hectare for
the construction of an artificial island for the development of the Hong
Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities (HKBCF), and about 19-hectare for the
southern landfall of the Tuen Mun - Chek Lap Kok Link (TMCLKL).
1.1.2
The
environmental impact assessment (EIA) reports (Hong Kong ¡V
Zhuhai ¡V Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing
Facilities ¡V EIA Report (Register No. AEIAR-145/2009) (HKBCFEIA) and Tuen Mun ¡V
Chek Lap Kok Link ¡V EIA Report (Register No. AEIAR-146/2009) (TMCLKLEIA), and
their environmental monitoring and audit (EM&A) Manuals (original EM&A
Manuals), for the Project were approved by Environmental Protection Department
(EPD) in October 2009.
1.1.3
EPD
subsequently issued the
Environmental Permit (EP) for HKBCF in November 2009
(EP-353/2009) and the Variation of Environmental Permit (VEP) in June 2010
(EP-353/2009/A), November 2010 (EP-353/2009/B), November 2011 (EP-353/2009/C), March 2012
(EP-353/2009/D) and October 2012 (EP-353/2009/E). Similarly, EPD issued the
Environmental Permit (EP) for TMCLKL in November 2009 (EP-354/2009) and the
Variation of Environmental Permit (VEP) in December 2010 (EP-354/2009/A).
1.1.4
The Project is a designated project and is governed by
the current permits for the Project, i.e. the amended EPs issued on 16 October
2012 (EP-353/2009/E) and 8 December 2011 (EP-354/2009/A) (for TMCLKL Southern
Landfall Reclamation only).
1.1.5
A Project Specific EM&A Manual, which included all
project-relation contents from the original EM&A Manuals for the Project,
was issued in May 2012.
1.1.6
Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Limited (Arup) was
appointed by Highways Department (HyD) as the consultants for the design and
construction assignment for the Project¡¦s reclamation works (i.e. the Engineer
for the Project).
1.1.7
China Harbour Engineering Company Limited (CHEC) was
awarded by HyD as the Contractor to undertake the construction work of the
Project.
1.1.8
ENVIRON Hong Kong Ltd. was employed by HyD as the
Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) and Environmental Project Office (ENPO)
for the Project.
1.1.9
AECOM Asia Co. Ltd. (AECOM) was appointed by CHEC to
undertake the role of Environmental Team for the Project for carrying out the
EM&A works.
1.1.10 The
construction phase of the Project under the EPs was commenced on 12 March 2012
and will be tentatively completed by early Year 2016.
1.1.11 According
to the Project Specific EM&A Manual, there is a need of an EM&A
programme including air quality, noise, water quality and dolphin monitoring
and environmental site inspections. The EM&A programme of the Project
commenced on 12 March 2012.
1.2
Scope
of Report
1.2.1
This is the eleventh monthly EM&A Report under the
Contract No. HY/2010/02 Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary
Crossing Facilities ¡V Reclamation Works.
This report presents a summary of the environmental monitoring and audit
works, list of activities and mitigation measures proposed by the ET for the
Project in January 2013.
1.3.1 The
project organization structure is shown in Appendix A. The key personnel
contact names and numbers are summarized in Table 1.1.
Table
1.1 Contact
Information of Key Personnel
|
Party
|
Position
|
Name
|
Telephone
|
Fax
|
|
Engineer¡¦s Representative (ER)
(Ove Arup
& Partners Hong Kong Limited)
|
Chief Resident Engineer
|
Michael Lo
|
2528 3031
|
2668 3970
|
|
IEC / ENPO
(ENVIRON Hong Kong Limited)
|
Independent Environmental Checker
|
Raymond Dai
|
3743 0788
|
3548 6988
|
|
Environmental Project Office Leader
|
Y. H. Hui
|
3743 0788
|
3548 6988
|
|
Contractor
(China Harbour Engineering Company
Limited)
|
General Manager (S&E)
|
Daniel Leung
|
3157 1086
|
2578 0413
|
|
Environmental Officer
|
C. M. Wong
|
3157 1086
|
2578 0413
|
|
24-hour Hotline
|
Alan C.C. Yeung
|
9448 0325
|
--
|
|
ET
(AECOM Asia
Company Limited)
|
ET Leader
|
Echo Leong
|
3922 9280
|
2317 7609
|
1.4.1 The construction phase of the Project under
the EP commenced on 12 March 2012.
1.4.2 As informed by the Contractor, details of
the major works carried out in this reporting period are listed below:-
Marine-based Works
-
Laying
geo-textile
-
Maintenance
of silt curtain
-
Stone
column installation
-
Cellular
structure installation
-
Band
drain installation
Land-based Works
-
Maintenance
works of Site Office at Works Area WA2
-
Maintenance
works of Public Works Regional Laboratory at Works Area
WA3
-
Sign
board erection at Works Area WA2
-
Geo-textile
fabrication at Works Area WA2
-
Stone
column installation barges setup and their maintenance works at Works Area WA4
-
Silt
curtain fabrication at Works Area WA4
1.4.3 The 3-month rolling construction programme
of the Project is shown in Appendix B.
1.4.4 The general layout plan of the Project site
showing the detailed works areas is shown in Figure 1.
1.4.5 The environmental mitigation measures
implementation schedule are presented in Appendix C.
1.5.1
The
EM&A programme required environmental monitoring for air quality, noise,
water quality, marine ecology and environmental site inspections for air
quality, noise, water quality, waste management, marine ecology, and landscape
and visual impact. The EM&A requirements for each parameter described in
the following sections include:-
-
All monitoring parameters;
-
Monitoring schedules for the reporting month
and forthcoming month;
-
Action and Limit levels for all environmental
parameters;
-
Event / Action Plan;
-
Environmental mitigation measures, as
recommended in the Project EIA reports; and
-
Environmental requirement in contract
documents.
2.1.1 In accordance with the Project Specific
EM&A Manual, baseline 1-hour and 24-hour Total Suspended Particulates (TSP)
levels at 4 air quality monitoring stations were established. Impact 1-hour TSP
monitoring was conducted for at least three times every 6 days, while impact
24-hour TSP monitoring was carried out for at least once every 6 days. The
Action and Limit level of the air quality monitoring is provided in Appendix D.
2.2.1 24-hour TSP air quality monitoring was
performed using High Volume Sampler (HVS) located at each designated monitoring
station. The HVS meets all the requirements of the Project Specific EM&A
Manual. Portable direct reading
dust meters were used to carry out the 1-hour TSP monitoring. Brand and model of the equipment is
given in Table 2.1.
Table
2.1 Air Quality
Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment
|
Brand and
Model
|
|
Portable direct
reading dust meter (1-hour TSP)
|
Sibata Digital
Dust Monitor (Model No. LD-3 and LD-3B)
|
|
High Volume
Sampler
(24-hour TSP)
|
Tisch
Environmental Mass Flow Controlled Total Suspended Particulate (TSP) High
Volume Air Sampler
(Model No.
TE-5170)
|
2.3
Monitoring Locations
2.3.1 Monitoring locations AMS2 and AMS7 were set
up at the proposed locations in accordance with Project Specific EM&A
Manual. For AMS6 (Dragonair/CNAC (Group) Building), permission on setting up
and carrying out impact monitoring works was sought, however, access to the
premise has not been granted yet on this report issuing date. For monitoring
location AMS3 (Ho Yu College), as proposed in the Project Specific EM&A
Manual, approval for carrying out impact monitoring could not be obtained from
the principal of the school. Permission on setting up and carrying out impact
monitoring works at nearby sensitive receivers, like Caribbean Coast and
Coastal Skyline, was also sought.
However, approvals for carrying out impact monitoring works within their
premises were not obtained. Impact air quality monitoring was conducted at site
boundary of the site office area in Works Area WA2 (AMS3A) respectively. Same
baseline and Action Level for air quality, as derived from the baseline
monitoring data recorded at Ho Yu College, was adopted for this alternative air
quality location.
2.3.2 Reference is made to ET¡¦s proposal
of the omission of air
monitoring station (AMS 6) dated on 1 November 2012 and EPD¡¦s letter dated on 19 November 2012
regarding the conditional approval of the proposed omission of air monitoring station (AMS 6)
for Contract No. HY/2010/02. The aforesaid omission of Monitoring Station AMS6 will be effective since 19 November 2012.
2.3.3 Figure 2 shows the locations of monitoring
stations. Table 2.2 describes the details of the monitoring stations.
Table 2.2 Locations
of Impact Air Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station
|
Location
|
Description
|
|
AMS2
|
Tung Chung
Development
Pier
|
Rooftop of the premise
|
|
AMS3A
|
Site Boundary
of Site Office
Area at Works
Area WA2
|
On ground at the area boundary
|
|
AMS6*
|
Dragonair/CNAC (Group) Building
|
On ground at boundary of the premise
|
|
AMS7
|
Hong Kong
SkyCity
Marriott Hotel
|
On ground at boundary of the premise
|
#Remarks: Reference is made
to EPD conditional approval of the omission of air monitoring station (AMS 6)
for the project. The omission will be effective on 19 November 2012.
2.4
Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and
Duration
2.4.1 Table 2.3 summarizes the monitoring parameters,
frequency and duration of impact TSP monitoring.
Table 2.3 Air
Quality Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and Duration
|
Parameter
|
Frequency and Duration
|
|
1-hour TSP
|
Three times every 6 days while the highest
dust impact was expected
|
|
24-hour TSP
|
Once every 6 days
|
2.5
Monitoring
Methodology
2.5.1 24-hour TSP Monitoring
(a)
The HVS was installed in the vicinity of the air
sensitive receivers. The following
criteria were considered in the installation of the HVS.
(i)
A horizontal platform with appropriate support to
secure the sampler against gusty wind was provided.
(ii)
No two samplers should be placed less than 2
meters apart.
(iii)
The distance between the HVS and any obstacles,
such as buildings, was at least twice the height that the obstacle protrudes above
the HVS.
(iv)
A minimum of 2 meters separation from walls,
parapets and penthouse for rooftop sampler.
(v)
A minimum of 2 meters separation from any
supporting structure, measured horizontally is required.
(vi)
No furnace or incinerator flues nearby.
(vii)
Airflow around the sampler was unrestricted.
(viii)
Permission was obtained to set up the samplers and
access to the monitoring stations.
(ix)
A secured supply of electricity was obtained to
operate the samplers.
(x)
The sampler was located more than 20 meters from
any dripline.
(xi)
Any wire fence and gate, required to protect the
sampler, did not obstruct the monitoring process.
(xii)
Flow control accuracy was kept within ¡Ó2.5%
deviation over 24-hour sampling period.
(b)
Preparation of Filter Papers
(i)
Glass fibre filters, G810 were labelled and sufficient
filters that were clean and without pinholes were selected.
(ii)
All filters were equilibrated in the conditioning
environment for 24 hours before weighing. The conditioning environment
temperature was around 25 ¢XC
and not variable by more than ¡Ó3 ¢XC;
the relative humidity (RH) was < 50% and not variable by more than ¡Ó5%. A
convenient working RH was 40%.
(iii)
All filter papers were prepared and analysed by ALS
Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd., which is a HOKLAS accredited laboratory and has
comprehensive quality assurance and quality control programmes.
(c)
Field Monitoring
(i)
The power supply was checked to ensure the HVS
works properly.
(ii)
The filter holder and the area surrounding the
filter were cleaned.
(iii)
The filter holder was removed by loosening the four
bolts and a new filter, with stamped number upward, on a supporting screen was
aligned carefully.
(iv)
The filter was properly aligned on the screen so
that the gasket formed an airtight seal on the outer edges of the filter.
(v)
The swing bolts were fastened to hold the filter holder
down to the frame. The pressure
applied was sufficient to avoid air leakage at the edges.
(vi)
Then the shelter lid was closed and was secured
with the aluminum strip.
(vii)
The HVS was warmed-up for about 5 minutes to
establish run-temperature conditions.
(viii)
A new flow rate record sheet was set into the flow
recorder.
(ix)
On site temperature and atmospheric pressure
readings were taken and the flow rate of the HVS was checked and adjusted at
around 1.1 m3/min, and complied with the range specified in the
updated EM&A Manual (i.e. 0.6-1.7 m3/min).
(x)
The programmable digital timer was set for a
sampling period of 24 hrs, and the starting time, weather condition and the
filter number were recorded.
(xi)
The initial elapsed time was recorded.
(xii)
At the end of sampling, on site temperature and
atmospheric pressure readings were taken and the final flow rate of the HVS was
checked and recorded.
(xiii)
The final elapsed time was recorded.
(xiv)
The sampled filter was removed carefully and folded
in half length so that only surfaces with collected particulate matter were in
contact.
(xv)
It was then placed in a clean plastic envelope and
sealed.
(xvi)
All monitoring information was recorded on a
standard data sheet.
(xvii)
Filters were then sent to ALS Technichem (HK) Pty
Ltd. for analysis.
(d)
Maintenance and Calibration
(i)
The HVS and its accessories were maintained in good
working condition, such as replacing motor brushes routinely and checking
electrical wiring to ensure a continuous power supply.
(ii)
5-point calibration of the HVS was conducted using
TE-5025A Calibration Kit prior
to the commencement of baseline monitoring. Bi-monthly 5-point calibration of
the HVS will be carried out during impact monitoring.
(iii)
Calibration certificate of the HVSs are provided in
Appendix E.
2.5.2 1-hour TSP Monitoring
(a)
Measuring Procedures
The measuring procedures of the 1-hour dust
meter were in accordance with the Manufacturer¡¦s Instruction Manual as
follows:-
(i)
Turn the power on.
(ii)
Close the air collecting opening cover.
(iii)
Push the ¡§TIME SETTING¡¨ switch to [BG].
(iv)
Push ¡§START/STOP¡¨ switch to perform background
measurement for 6 seconds.
(v)
Turn the knob at SENSI ADJ position to insert the
light scattering plate.
(vi)
Leave the equipment for 1 minute upon ¡§SPAN CHECK¡¨
is indicated in the display.
(vii)
Push ¡§START/STOP¡¨ switch to perform automatic
sensitivity adjustment. This measurement takes 1 minute.
(viii)
Pull out the knob and return it to MEASURE
position.
(ix)
Push the ¡§TIME SETTING¡¨ switch the time set in the
display to 3 hours.
(x)
Lower down the air collection opening cover.
(xi)
Push ¡§START/STOP¡¨ switch to start measurement.
(b)
Maintenance and Calibration
(i)
The 1-hour TSP meter was calibrated at 1-year
intervals against a continuous particulate TEOM Monitor, Series 1400ab.
Calibration certificates of the Laser Dust Monitors are provided in Appendix E.
(ii)
1-hour validation checking of the TSP meter against
HVS is carried out on half-year
basis
at the air quality monitoring locations.
2.6
Monitoring Schedule for the Reporting Month
2.6.1
The
schedule for air quality monitoring in January 2013 is provided in Appendix F.
2.7
Results and Observations
2.7.1 The monitoring results for 1-hour TSP and
24-hour TSP are summarized in Table 2.4 and 2.5 respectively. Detailed impact
air quality monitoring results are presented in Appendix G.
Table 2.4 Summary
of 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
|
Average (mg/m3)
|
Range (mg/m3)
|
Action Level (mg/m3)
|
Limit Level (mg/m3)
|
|
AMS2
|
85
|
80 ¡V 92
|
374
|
500
|
|
AMS3A
|
87
|
81 ¡V 96
|
368
|
500
|
|
AMS7
|
85
|
81 - 89
|
370
|
500
|
Table 2.5 Summary
of 24-hour TSP Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
|
Average (mg/m3)
|
Range (mg/m3)
|
Action Level (mg/m3)
|
Limit Level (mg/m3)
|
|
AMS2
|
98
|
74 - 138
|
176
|
260
|
|
AMS3A
|
127
|
89 - 163
|
167
|
260
|
|
AMS7
|
124
|
98 - 154
|
183
|
260
|
2.7.2 The major dust source in the reporting
period included construction activities from the Project, construction
activities by other contacts, as well as nearby traffic emissions.
2.7.3 All 1-hour TSP and 24-hour
TSP results were below the
Action and Limit Level at all monitoring locations in the reporting month.
2.7.4 The event action plan is annexed in Appendix
L.
2.7.5 Meteorological information collected from
the wind station during the monitoring periods on the monitoring dates, as
shown in Figure 2, including wind speed and wind direction, is annexed in
Appendix H.
3.1.1 In accordance with the Project Specific
EM&A Manual, impact noise monitoring was conducted for at least once per
week during the construction phase of the Project. The Action and Limit level
of the noise monitoring is provided in Appendix D.
3.2
Monitoring Equipment
3.2.1 Noise monitoring was performed using sound
level meter at each designated monitoring station. The sound level meters deployed comply
with the International Electrotechnical Commission Publications (IEC) 651:1979
(Type 1) and 804:1985 (Type 1) specifications. Acoustic calibrator was deployed to
check the sound level meters at a known sound pressure level. Brand and model of the equipment is
given in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 Noise
Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment
|
Brand and Model
|
|
Integrated Sound Level Meter
|
Rion NL-31
|
|
Acoustic Calibrator
|
Rion NC-73
|
3.3
Monitoring Locations
3.3.1 Monitoring locations NMS2 was set up at the proposed
locations in accordance with Project Specific EM&A Manual. However, for
monitoring location NMS3 (Ho Yu College), as proposed in the Project Specific
EM&A Manual, approval for carrying out impact monitoring could not be
obtained from the principal of the school. Permission on setting up and
carrying out impact monitoring works at nearby sensitive receivers, like
Caribbean Coast and Coastal Skyline, was also sought. However, approvals for carrying out impact
monitoring works within their premises were not obtained. Impact noise
monitoring was conducted at site boundary of the site office area in Works Area
WA2 (NMS3A) respectively. Same baseline noise level (as derived from the
baseline monitoring data recorded at Ho Yu College) and Limit Level were
adopted for this alternative noise monitoring location.
Remarks: Monitoring
3.3.2 Figure 2 shows the locations of the
monitoring stations. Table 3.2 describes the details of the monitoring
stations.
Table
3.2 Locations
of Impact Noise Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station
|
Location
|
Description
|
|
NMS2
|
Seaview Crescent Tower 1
|
Free-field on
the rooftop of the premise
|
|
NMS3A
|
Site Boundary of Site Office Area at Works Area WA2
|
Free-field on ground at the area boundary.
|
3.4.1
Table
3.3 summarizes the monitoring parameters, frequency and duration of impact
noise monitoring.
Table 3.3 Noise
Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and Duration
|
Parameter
|
Frequency and
Duration
|
|
30-mins
measurement at each monitoring station between 0700 and 1900 on normal
weekdays (Monday to Saturday). Leq, L10 and L90
would be recorded.
|
At least once per week
|
3.5.1 Monitoring Procedure
(a)
The sound level meter was set on a tripod at a
height of 1.2 m above
the ground for free-field measurements at NMS2. A correction of +3 dB(A) shall
be made to the free field measurements.
(b)
All measurement at NMS3A
were free
field measurements in the reporting month at NMS3A. A correction of
+3 dB(A) shall be made to the free field measurements.
(c)
The battery condition was checked to ensure the
correct functioning of the meter.
(d)
Parameters such as frequency weighting, the time
weighting and the measurement time were set as follows:-
(i)
frequency weighting: A
(ii)
time weighting: Fast
(iii)
time measurement: Leq(30-minutes) during
non-restricted hours i.e. 07:00 ¡V 1900 on normal weekdays.
(e)
Prior to and after each noise measurement, the
meter was calibrated using the acoustic calibrator for 94dB(A) at 1000 Hz. If the difference in the calibration
level before and after measurement was more than 1 dB(A), the measurement would
be considered invalid and repeat of noise measurement would be required after
re-calibration or repair of the equipment.
(f)
During the monitoring period, the Leq, L10
and L90 were recorded.
In addition, site conditions and noise sources were recorded on a
standard record sheet.
(g)
Noise measurement was paused during periods of high
intrusive noise (e.g. dog barking, helicopter noise) if possible. Observations
were recorded when intrusive noise was unavoidable.
(h)
Noise monitoring was cancelled in the presence of
fog, rain, wind with a steady speed exceeding 5m/s, or wind with gusts exceeding 10m/s. The wind speed shall be checked with a portable wind speed meter
capable of measuring the wind speed in m/s.
3.5.2 Maintenance and Calibration
(a)
The microphone head of the sound level meter was
cleaned with soft cloth at regular intervals.
(b)
The meter and calibrator were sent to the supplier
or HOKLAS laboratory to check and calibrate at yearly intervals.
(c)
Calibration certificates of the sound level meters
and acoustic calibrators are provided in Appendix E.
3.6.1 The schedule for construction noise
monitoring in January 2013 is provided
in Appendix F.
3.7.1 The monitoring results for construction
noise are summarized in Table 3.4 and the monitoring data is provided in
Appendix I.
Table
3.4 Summary
of Construction Noise Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
|
Average, dB(A),
Leq
(30 mins)
|
Range, dB(A),
Leq
(30 mins)
|
Limit Level, dB(A),
Leq
(30 mins)
|
|
NMS2
|
66*
|
64
¡V 68*
|
75
|
|
NMS3A
|
65*
|
63
¡V 66*
|
70^
|
*+3dB(A) Façade correction included
^
Daytime noise Limit Level of 70 dB(A) applies to education institutions
3.7.2 No noise Action Level and Limit Level
exceedance was recorded at all monitoring stations in the reporting month.
3.7.3 Major noise sources during the noise
monitoring included construction activities of the Project, construction
activities by other contracts and nearby traffic noise.
3.7.4 The event action plan is annexed in Appendix
L.
4
WATER QUALITY MONITORING
4.1
Monitoring Requirements
4.1.1 Impact water quality monitoring was carried out
to ensure that any deterioration of water quality was detected, and that timely
action was taken to rectify the situation.
For impact water quality monitoring, measurements were taken in
accordance with the Project Specific EM&A Manual. Appendix D shows the
established Action/Limit Levels for the environmental monitoring works.
4.2.1 Table 4.1 summarises the equipment used in
the impact water quality monitoring programme.
Table 4.1 Water
Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment
|
Brand and
Model
|
|
Dissolved Oxygen
(DO) and Temperature Meter, Salinity Meter and Turbidimeter
|
YSI Model 6820
|
|
pH Meter
|
YSI Model 6820 or
Thermo Orion 230A+
|
|
Positioning
Equipment
|
JRC DGPS 224
Model JLR-4341 with J-NAV 500 Model NWZ4551
|
|
Water Depth
Detector
|
Eagle Cuda-168
|
|
Water Sampler
|
Kahlsio Water
Sampler (Vertical) 2.2 L with messenger
|
4.3.1
Table
4.2 summarises the monitoring parameters, frequency and monitoring depths of
impact water quality monitoring as required in the Project Specific EM&A
Manual.
Table 4.2 Impact
Water Quality Monitoring Parameters and Frequency
|
Monitoring Stations
|
Parameter, unit
|
Frequency
|
No. of depth
|
|
Impact Stations:
IS5, IS(Mf)6, IS7, IS8, IS(Mf)9, IS10, IS(Mf)11, IS(Mf)16, IS17
Control/Far Field Stations:
CS(Mf)3, CS(Mf)5, CS4, CS6, CSA
Sensitive Receiver Stations:
SR3-SR7, SR10A&SR10B
|
¡P
Depth, m
¡P
Temperature, oC
¡P
Salinity,
ppt
¡P
Dissolved Oxygen (DO), mg/L
¡P
DO Saturation, %
¡P
Turbidity, NTU
¡P
pH
¡P
Suspended Solids (SS), mg/L
|
Three times per week during
mid-ebb and mid-flood tides (within ¡Ó 1.75 hour of the predicted time)
|
3
(1 m below water surface,
mid-depth and 1 m above sea bed, except where the water depth is less than 6
m, in which case the mid-depth station may be omitted. Should the water
depth be less than 3 m, only the mid-depth station will be monitored).
|
4.4.1 In accordance with the Project Specific
EM&A Manual, twenty-one stations (9 Impact Stations, 7 Sensitive Receiver
Stations and 5 Control/Far Field Stations) were designated for impact water
quality monitoring. The nine Impact Stations (IS) were chosen on the basis of
their proximity to the reclamation and thus the greatest potential for water
quality impacts, the seven Sensitive Receiver Stations (SR) were chosen as they
are close to the key sensitive receives and the five Control/ Far Field
Stations (CS) were chosen to facilitate comparison of the water quality of the
IS stations with less influence by the Project/ ambient water quality
conditions.
4.4.2 Due to safety concern and topographical
condition of the original locations of SR4 and SR10B, alternative impact water quality
monitoring stations, naming as SR4(N) and SR10B(N), were adopted, which are
situated in vicinity of the original impact water quality monitoring stations
(SR4 and SR10B) and could be reachable.
4.4.3 Same baseline and Action Level for water
quality, as derived from the baseline monitoring data recorded, were adopted
for these alternative impact water quality monitoring stations.
4.4.4 The locations of these monitoring stations
are summarized in Table 4.3 and depicted in Figure 3.
Table
4.3 Impact
Water Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Station
|
Description
|
East
|
North
|
|
IS5
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
811579
|
817106
|
|
IS(Mf)6
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
812101
|
817873
|
|
IS7
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
812244
|
818777
|
|
IS8
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
814251
|
818412
|
|
IS(Mf)9
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
813273
|
818850
|
|
IS10
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
812577
|
820670
|
|
IS(Mf)11
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
813562
|
820716
|
|
IS(Mf)16
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
814328
|
819497
|
|
IS17
|
Impact Station (Close to HKBCF construction site)
|
814539
|
820391
|
|
SR3
|
Sensitive receivers (San Tau SSSI)
|
810525
|
816456
|
|
SR4(N)
|
Sensitive receivers (Tai Ho)
|
814705
|
817859
|
|
SR5
|
Sensitive receivers (Artificial Reef in NE Airport)
|
811489
|
820455
|
|
SR6
|
Sensitive receivers (Sha Chau and Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park)
|
805837
|
821818
|
|
SR7
|
Sensitive receivers (Tai Mo Do)
|
814293
|
821431
|
|
SR10A
|
Sensitive receivers (Ma Wan FCZ)1
|
823741
|
823495
|
|
SR10B(N)
|
Sensitive receivers (Ma Wan FCZ)2
|
823683
|
823187
|
|
CS(Mf)3
|
Control Station
|
809989
|
821117
|
|
CS(Mf)5
|
Control Station
|
817990
|
821129
|
|
CS4
|
Control Station
|
810025
|
824004
|
|
CS6
|
Control Station
|
817028
|
823992
|
|
CSA
|
Control Station
|
818103
|
823064
|
4.5.1 Instrumentation
(a)
The in-situ water quality parameters, viz.
dissolved oxygen, temperature, salinity, turbidity and pH, were measured by multi-parameter
meters (i.e. Model YSI 6820 CE-C-M-Y) and pH meter (i.e. Thermo Orion 230A+) respectively.
4.5.2 Operating/Analytical Procedures
(a)
Digital
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPS) were used to ensure that the correct location
was selected prior to sample collection.
(b)
Portable, battery-operated echo sounders were used
for the determination of water depth at each designated monitoring station.
(c)
All in-situ measurements were taken at 3 water
depths, 1 m below water
surface, mid-depth and 1 m above sea bed, except where the water depth was less
than 6 m, in which case the mid-depth station was omitted. Should the
water depth be less than 3 m, only the mid-depth station was monitored.
(d)
At each measurement/sampling depth, two consecutive
in-situ monitoring (DO concentration and saturation, temperature, turbidity,
pH, salinity) and water sample for SS. The probes were retrieved out of the
water after the first measurement and then re-deployed for the second
measurement. Where the difference in the value between the first and second
readings of DO or turbidity parameters was more than 25% of the value of the
first reading, the reading was discarded and further readings were taken.
(e)
Duplicate samples from each independent sampling
event were collected for SS measurement. Water samples were collected using the
water samplers and the samples were stored in high-density polythene bottles.
Water samples collected were well-mixed in the water sampler prior to
pre-rinsing and transferring to sample bottles. Sample bottles were pre-rinsed
with the same water samples. The sample bottles were then be packed in
cool-boxes (cooled at 4oC without being frozen), and delivered to
ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. for the analysis of suspended solids concentrations.
The laboratory determination work would be started within 24 hours after
collection of the water samples. ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. is a HOKLAS
accredited laboratory and has comprehensive quality assurance and quality
control programmes. For QA/QC procedures, one duplicate samples of every batch
of 20 samples was analyzed.
(f)
The analysis method and reporting and detection
limit for SS is shown in Table 4.4.
Table
4.4 Laboratory
Analysis for Suspended Solids
|
Parameters
|
Instrumentation
|
Analytical Method
|
Reporting Limit
|
Detection Limit
|
|
Suspended
Solid (SS)
|
Weighting
|
APHA 2540-D
|
0.5mg/L
|
0.5mg/L
|
(g)
Other relevant data were recorded, including
monitoring location / position, time, water depth, tidal stages, weather conditions
and any special phenomena or work underway at the construction site in the
field log sheet for
information.
4.5.3 Maintenance and Calibration
(a)
All in situ monitoring instruments would be
calibrated and calibrated by ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. before use and at
3-monthly intervals throughout all stages of the water quality monitoring programme. Calibration details are provided in Appendix E.
(b)
The dissolved oxygen probe of YSI 6820 was
calibrated by wet bulb method. Before the calibration routine, the sensor for
dissolved oxygen was thermally equilibrated in water-saturated air. Calibration
cup is served as a calibration chamber and it was loosened from airtight
condition before it is used for the calibration. Calibration at ALS Technichem
(HK) Pty Ltd. was carried out once every three months in a water sample with a
known concentration of dissolved oxygen. The sensor was immersed in the water
and after thermal equilibration, the known mg/L value was keyed in and the
calibration was carried out automatically.
(c)
The turbidity probe of YSI 6820 is calibrated two
times a month. A zero check in distilled water was performed with the turbidity
probe of YSI 6820 once per monitoring day. The probe will be calibrated with a
solution of known NTU at ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. once every three months.
4.6
Monitoring
Schedule for the Reporting Month
4.6.1 The schedule for impact water quality
monitoring in January 2013 is provided
in Appendix F.
4.7.1 Impact water quality monitoring results and
graphical presentations are provided in Appendix J.
4.7.2 Total of
Six (6) Acton Level exceedances at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) were
recorded during the reporting month. Number of exceedances
recorded in the reporting month at each impact station is summarized in Table 4.5
Table 4.5 Summary
of Water Quality Exceedances
|
Station
|
Exceedance Level
|
DO (S&M)
|
DO (Bottom)
|
Turbidity
|
SS
|
Total
|
|
Ebb
|
Flood
|
Ebb
|
Flood
|
Ebb
|
Flood
|
Ebb
|
Flood
|
Ebb
|
Flood
|
|
IS5
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS(Mf)6
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS7
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS8
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS(Mf)9
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS10
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
(2 Jan, 13)
|
0
|
1
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS(Mf)11
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS(Mf)16
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
(4 Jan, 13)
|
0
|
1
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
IS17
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR3
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR4(N)
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR5
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
2
(11 & 30 Jan, 13)
|
0
|
2
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR6
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
2
(2 and 14 Jan, 13)
|
0
|
2
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR7
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR10A
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SR10B
(N)
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Total
|
Action
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
6
(2, 3, 11, 14 and 30 Jan 13)
|
|
|
Limit
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
Note: S: Surface;
and
M:
Mid-depth.
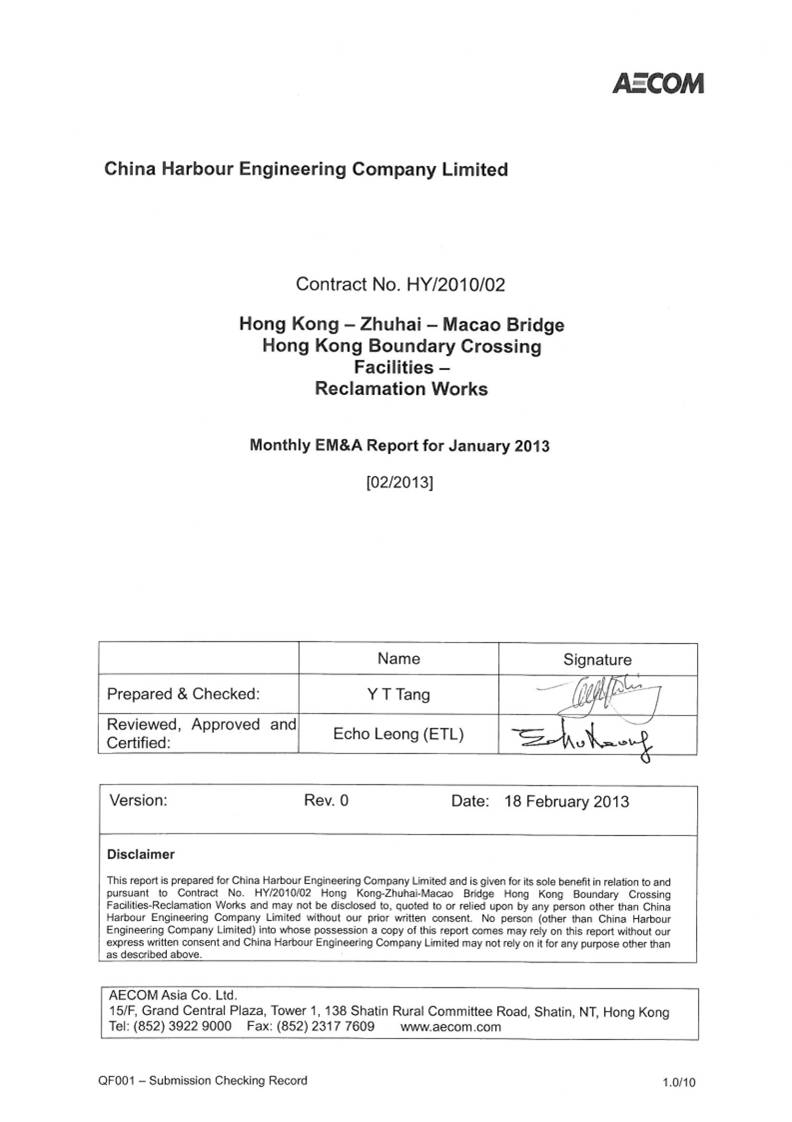
4.7.3 Two (2)
Acton Level exceedances at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) were recorded on 02 Jan 2013 during mid-flood tide at monitoring station IS10 and SR6. For
Action Level exceedances at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L), 28.2 mg/L and
25.7 mg/L were recorded at
Monitoring Station IS10 and
SR6 respectively.
4.7.3.1 For
the exceedances recorded at IS10 and SR6, it was found that Stone column
installation was carried out throughout the day at Portion D by AP1 and AP2, at
Portion A by FTB20, at Portion A by AP3 and Portion C2C by FTB18.
4.7.3.2 Same
type of works were carried out at the same location on 31 Dec 12 and 4 Jan 13
but Suspended Solids values recorded at IS10 and SR6 on 31 Dec 12 and 4 Jan 13
are all below the Action and Limit Level during the same tide on the same day.
4.7.3.3 Suspended
solids values recorded at Impact Stations IS(Mf)11 which is closer to the works
area than Impact Station IS10 were below the action and limit level.
4.7.3.4 Suspended
solids values recorded at Impact Stations SR5 and CS(Mf)3 located downstream of
monitoring station IS10 during mid-flood tide was below the action and limit
level.
4.7.3.5 Suspended
Suspended solids values recorded at Impact Stations SR5 and CS(Mf)3 which are
closer to the works area than SR 6 were below the action and limit level.
4.7.3.6 The
exceedances were likely due to local effects in the vicinity of IS10 and SR6.
4.7.3.7 The exceedances were considered as
non-Project related.
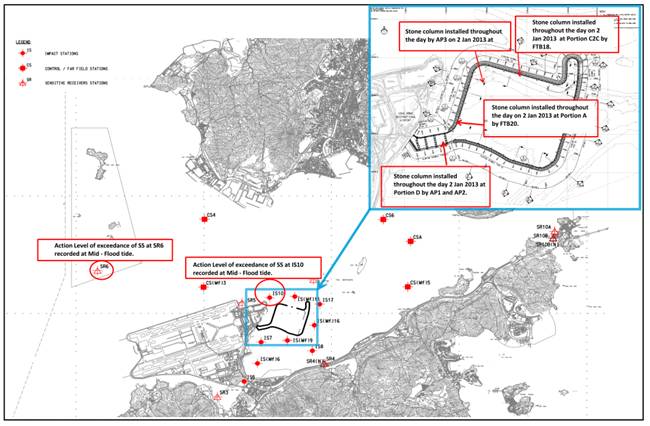
4.7.4 One (1)
Acton Level exceedance at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) was recorded on 04 Jan 2013 during mid-flood tide at Impact Station IS(Mf)16. For the Action Level exceedance of
measured Suspended Solids (mg/L), 23.9 mg/L was recorded at Impact Station IS(Mf)16 during mid-flood tide.
4.7.4.1 For
Action Level Exceedance recorded at Impact Station IS(Mf)16 during mid-flood
tide, stone column installation was carried out
throughout the day at Portion D by FTB 16, AP1 and AP2, at Portion A by FTB20,
at Portion A by AP3 and Portion C2C by FTB18.
4.7.4.2 Suspended
Solids values recorded at Impact Station IS(Mf)9 and IS7 which are closer to
the works than monitoring station IS(Mf)6 are all below the Action and Limit
Level during the same tide on the same day.
4.7.4.3 Impact
Stations IS10 and IS(Mf)11 which are considered downstream and closer to the
works than Impact Station IS(Mf)16. Since the Suspended Solids values recorded
at IS10 and IS(Mf)11 are all below
the Action and Limit Level during same tide on the same day. The water quality
noted at downstream of active works were not adversely affected by active
works. Hence it is considered that the exceedance recorded at IS(Mf)16 located
upstream of active works are not related to the Project.
4.7.4.4 IS(Mf)16
is considered upstream of Partion D, A and C2C where work was carried out during mid
flood tide.
4.7.4.5 The
exceedance was likely due to local effects in the vicinity of IS(Mf)16.
4.7.4.6 The
exceedance was considered as Non-Project Related.
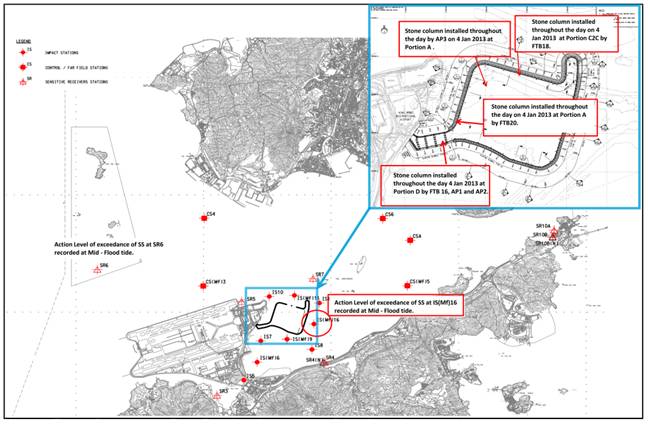
4.7.5 One (1)
Acton Level exceedance at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) was recorded on 11 Jan 2013 at monitoring station SR5
during mid-flood tide. For Action Level exceedance of measured Suspended Solids
(mg/L), 30.1 mg/L were recorded at monitoring station SR5 during mid-flood
tide.
4.7.5.1 For
Action Level Exceedance of SS recorded
at
monitoring station SR5 during
mid-flood tide at monitoring station SR5 recorded on 11 Jan 2013, stone column installation was carried out throughout the
day at Portion D by FTB16, FTB20, AP1 and AP2, at Portion A by FTB19 and AP3,
at Portion C2A by FTB17 and Portion C2c by FTB18.
4.7.5.2 Impact
Stations IS10 and IS(Mf)11 which are considered downstream and closer to the
works than Impact Station SR5. Since the Suspended Solids values recorded at IS10
and IS(Mf)11 are all below the Action and Limit Level during same tide on the
same day. The water quality noted at downstream of and closer to active works
were not adversely affected by active works.Hence it is considered that the
exceedance recorded at SR5 are not related to the Project.
4.7.5.3 Same
type of works was carried out at almost the same location on 9 and 14 January13
but Suspended Solids values recorded at SR5 on 9 and 14 January 13 are all
below the Action and Limit Level during the same tide on the same day.
4.7.5.4 The
exceedance was likely due to local effects in the vicinity of SR5.
4.7.5.5 The
exceedance was considered as Non-Project Related.
4.7.6 One (1)
action Level exceedance at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) was recorded on 14 Jan 2013 at monitoring station SR6
during mid-flood tide. For Action Level exceedance of measured Suspended Solids
(mg/L), 33.8 mg/L were recorded at monitoring station SR5 during mid-flood
tide.
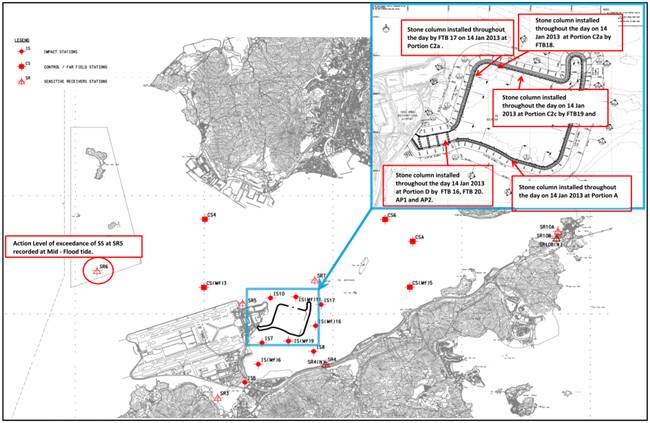
4.7.6.1 For Action
Level Exceedance of SS at IS(Mf)6 at Mid-Flood tide recorded on 14 Jan 2013 at
monitoring station SR6 during mid-flood tide, s tone column installation was
carried out throughout the day at Portion D by FTB 16, FTB20, AP1 and AP2, at
Portion A by FTB19 and AP3, at Portion C2A by FTB17 and Portion C2c by FTB18.
4.7.6.2 Impact
Stations IS10, IS(Mf)11, SR5 and CS(Mf)3 which are considered downstream and
closer to active works than Monitoring Station SR6. Since the Suspended Solids
values recorded at IS10, IS(Mf)11, SR5 and CS(Mf)3 are all below the Action and
Limit Level during same tide on the same day. The water quality noted at
downstream of and closer to active works were not adversely affected by active
works. Hence it is considered that the exceedance recorded at SR6 is not
related to the Project.
4.7.6.3 Same type
of works was carried out at almost the same location on 11 and 16 January13 but
Suspended Solids values recorded at SR6 on 11 and 16 January 13 are all below
the Action and Limit Level during the same tide on the same day.
4.7.6.4 The
exceedance was likely due to local effects in the vicinity of SR6.
4.7.6.5 The exceedance was considered as Non-Project
Related.
4.7.7 One (1)
action Level exceedance at measured Suspended Solids (mg/L) was recorded on 30 Jan 2013 at monitoring station SR5
during mid-flood tide. For Action Level exceedance of measured Suspended Solids
(mg/L), 30.1 mg/L were recorded at monitoring station SR5 during mid-flood
tide.
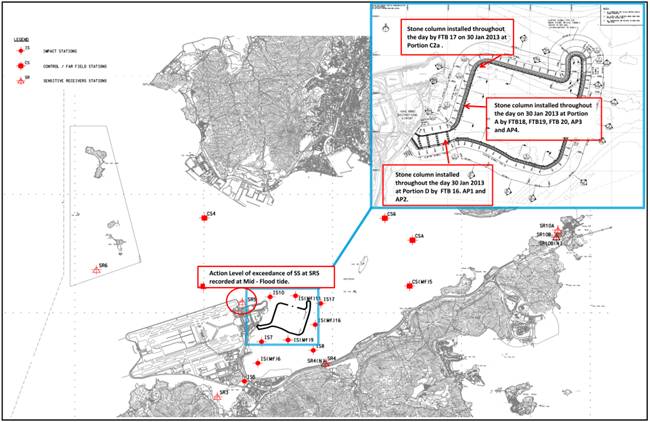
4.7.7.1 For Action
Level Exceedance of SS recorded at Mid-Flood tide on 30 Jan 2013 at monitoring
station SR5, Stone column installation was carried out throughout the day at
Portion D by FTB 16, AP1 and AP2, at Portion A by FTB 18, FTB19, FTB20, AP3 and
AP4, at Portion C2A by FTB17.
4.7.7.2 Impact
Stations IS10 and IS(Mf)11 which are considered downstream and closer to the
works than Impact Station SR5. Since the Suspended Solids values recorded at
IS10 and IS(Mf)11 are all below the Action and Limit Level during same tide on
the same day. The water quality noted at downstream of and closer to active
works were not adversely affected by active works. Hence it is considered that
the exceedance recorded at SR5 is not related to the Project.
4.7.7.3 Same type
of works was carried out at almost the same location on 28 Jan13 and 01 Feb13
but Suspended Solids values recorded at SR5 on 28 Jan13 and 01 Feb13 are all
below the Action and Limit Level during the same tide on the same day.
4.7.7.4 The
exceedance was likely due to local effects in the vicinity of SR5.
4.7.7.5 The exceedance was considered as Non-Project
Related.
4.7.7.6 The floating type silt curtains were provided
around the whole works area. However, integrity checking record of 30 Jan 13
shows that defects were found at parts of the floating type silt curtains. The
Contractor was reminded to swiftly rectify the perimeter silt curtain in
particular the portions which defects were observed to ensure the sediment
plume generated by construction activities could be prevented from discharging to
areas outside the site boundary.
4.7.7.7 As informed by the Contractor, maintenance
work of the silt curtain was carried out on a daily basis except Sunday.
4.7.8 The event action plan is annexed in Appendix
L.
5
Dolphin
monitoring
5.1.2
This
¡¥Impact Monitoring¡¦ follows several months of ¡¥Baseline Monitoring¡¦ so similar
survey methodologies have been adopted to facilitate comparisons between
datasets. Further, the data
collected are compatible with, and are available for, incorporation into the
data set managed by the Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department
(AFCD) as part of Hong Kong¡¦s long term Marine Mammal Monitoring Programme.
5.2
Monitoring Equipment
5.2.1 Table 5.1 summarises the equipment used for
the impact dolphin monitoring.
Table 5.1 Dolphin
Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment
|
Model
|
|
Commercially licensed motor vessel
|
15m in length
with a 4.5m viewing platform
|
|
Global
Positioning System (GPS) x2
|
Garmin 18X-PC
Geo One Phottix
|
|
Computers
(Corei7) x2
|
Windows /MSO 10
Logger
|
|
AIS receiver
|
Logger ¡V GPS
linked
|
|
Camera
|
Nikon D90 300m 2.8D fixed focus
Nikon D90 20-300m zoom lens
|
|
Laser Rangefinder
|
Infinitor
LRF1000/Visionking 900
|
|
Marine Binocular
x3
|
Nexus 7 x 50 marine binocular with
compass and reticules
Fujinon 7 x 50 marine binocular with
compass and reticules
|
5.3.1 Dolphin monitoring is conducted twice per
month in each survey area.
5.3.2 Dolphin monitoring is conducted only when
visibility is good (e.g., over 1km) and the sea condition is at a Beaufort Sea
State of 4 or better.
5.3.3 When thunder storm, black rain or typhoon
warnings are in force, all survey effort is stopped.
5.4.1 The impact dolphin monitoring is
vessel-based and combines line-transect and photo-ID methodology. The survey follows pre-set and fixed
transect lines in the two areas defined by AFCD as:
Northeast Lantau survey area; and
Northwest Lantau survey area.
5.4.2 The co-ordinates for the transect lines and
layout map have been provided by AFCD and are shown in Table 5.2 and Figure 4.
Table 5.2 Impact
Dolphin Monitoring Line Transect Co-ordinates (Provided by AFCD)
|
|
HK
Grid System
|
Long
Lat in WGS84
|
|
ID
|
X
|
Y
|
Long
|
Lat
|
|
1
|
804671
|
814577
|
113.870308
|
22.269741
|
|
1
|
804671
|
831404
|
113.869975
|
22.421696
|
|
2
|
805475
|
815457
|
113.878087
|
22.277704
|
|
2
|
805477
|
826654
|
113.877896
|
22.378814
|
|
3
|
806464
|
819435
|
113.887615
|
22.313643
|
|
3
|
806464
|
822911
|
113.887550
|
22.345030
|
|
4
|
807518
|
819771
|
113.897833
|
22.316697
|
|
4
|
807518
|
829230
|
113.897663
|
22.402113
|
|
5
|
808504
|
820220
|
113.907397
|
22.320761
|
|
5
|
808504
|
828602
|
113.907252
|
22.396462
|
|
6
|
809490
|
820466
|
113.916965
|
22.323003
|
|
6
|
809490
|
825352
|
113.916884
|
22.367128
|
|
7
|
810499
|
820690
|
113.926752
|
22.325043
|
|
7
|
810499
|
824613
|
113.926688
|
22.360464
|
|
8
|
811508
|
820847
|
113.936539
|
22.326475
|
|
8
|
811508
|
824254
|
113.936486
|
22.357241
|
|
9
|
812516
|
820892
|
113.946329
|
22.326894
|
|
9
|
812516
|
824254
|
113.946279
|
22.357255
|
|
10*
|
813525
|
818270
|
113.956156
|
22.303225
|
|
10*
|
813525
|
824657
|
113.956065
|
22.360912
|
|
11
|
814556
|
818449
|
113.966160
|
22.304858
|
|
11
|
814556
|
820992
|
113.966125
|
22.327820
|
|
12
|
815542
|
818807
|
113.975726
|
22.308109
|
|
12
|
815542
|
824882
|
113.975647
|
22.362962
|
|
13
|
816506
|
819480
|
113.985072
|
22.314192
|
|
13
|
816506
|
824859
|
113.985005
|
22.362771
|
|
14
|
817537
|
820220
|
113.995070
|
22.320883
|
|
14
|
817537
|
824613
|
113.995018
|
22.360556
|
|
15
|
818568
|
820735
|
114.005071
|
22.325550
|
|
15
|
818568
|
824433
|
114.005030
|
22.358947
|
|
16
|
819532
|
821420
|
114.014420
|
22.331747
|
|
16
|
819532
|
824209
|
114.014390
|
22.356933
|
|
17
|
820451
|
822125
|
114.023333
|
22.338117
|
|
17
|
820451
|
823671
|
114.023317
|
22.352084
|
|
18
|
821504
|
822371
|
114.033556
|
22.340353
|
|
18
|
821504
|
823761
|
114.033544
|
22.352903
|
|
19
|
822513
|
823268
|
114.043340
|
22.348458
|
|
19
|
822513
|
824321
|
114.043331
|
22.357971
|
|
20
|
823477
|
823402
|
114.052695
|
22.349680
|
|
20
|
823477
|
824613
|
114.052686
|
22.360610
|
|
21
|
805476
|
827081
|
113.877878
|
22.382668
|
|
21
|
805476
|
830562
|
113.877811
|
22.414103
|
|
22
|
806464
|
824033
|
113.887520
|
22.355164
|
|
22
|
806464
|
829598
|
113.887416
|
22.405423
|
|
23
|
814559
|
821739
|
113.966142
|
22.334574
|
|
23
|
814559
|
824768
|
113.966101
|
22.361920
|
*Remark: Due to the
presence of deployed silt curtain systems at the site boundaries of the
Project, some of the transect lines shown in Figure 5 could not be fully surveyed
during the regular survey. Transect 10 is reduced from 6.4km to approximately
3.6km in length due to the HKBCF construction site. Therefore the total
transect length for both NEL and NWL combined is reduced to approximately
111km.
5.5.1 The study area incorporates 23 transects
which are to be surveyed twice per month.
Each survey day lasts approximately 9 hours.
5.5.2 The survey vessel departs from Tung Chung
Development Pier, Tsing Yi Public Pier or the nearest safe and convenient
pier.
5.5.3 When the vessel reaches the start of a
transect line, ¡§on effort¡¨ survey begins. Areas between transect lines and
traveling to and from the study area are defined as ¡§off effort¡¨.
5.5.4 The transect line is surveyed at a speed of
6-8 knots (11-14 km/hr). For the sake of safety, the speed was sometimes a bit
slower to avoid collision with other vessels. During some periods, tide and current
flow in the survey areas exceeds 7 knots which can affect survey speed. There
are a minimum of four marine mammal observers (MMOs) present on each survey,
rotating through four positions, observers (2), data recorder (1) and ¡¥rest¡¦
(1). Rotations occur every 30 minutes or at the end of dolphin encounters. The data recorder records effort,
weather and sightings data directly onto the programme Logger and is not
part of the observer team. The observers search with naked eye and
binoculars between 90¢X and 270¢X abeam (bow being 0¢X).
5.5.5 When a group of dolphins is sighted, position,
bearing and distance data are recorded immediately onto the computer and, after
a short observation, an estimate made of group size. These parameters are linked to the
time-GPS-ships data which are automatically stored in the programme Logger throughout
the survey period. In this manner,
information on heading, position, speed, weather, effort and sightings are
stored in a format suitable for use with DISTANCE software for subsequent line
transect analyses.
5.5.6 Once the vessel leaves the transect line, it
is deemed to be ¡§off effort¡¨. The dolphins are approached with the purpose of
taking high resolution pictures for proper photo-identification of individual
CWD. Attempts to photograph all
dolphins in the group are made.
Both the left and right hand sides of the dorsal fin area of each
dolphin in the group are photographed, if possible. On finishing photographing, the vessel
will return to the transect line at the point of departure and ¡§on effort¡¨ survey
is resumed.
5.5.7 Sightings which are made while on the
transect line are referred to as "on effort sightings", while not on
the actual transect line are referred to as an ¡§opportunistic sightings¡¨ (e.g.
another group of dolphins is sighted while travelling back to the transect
line). Only ¡§on effort sightings¡¨
can be used in analyses which require effort or rate quantification, e.g.,
encounter rate per 100km searched.
This is also how ¡§on effort sightings¡¨ are treated in the baseline
report. ¡§Opportunistic sightings¡¨
provide additional information on individual habitat use and population
distribution and they are noted accordingly.
5.5.8 As time and GPS data are automatically
logged throughout the survey and are linked to sightings data input, start and
end times of encounters and deviation from the transect lines are recorded and
can be subsequently reviewed.
5.7
Results and Observations
5.7.1 Dolphin surveys were conducted on 8, 9, 28 and 29 January 2013. In summary, a total of 222.2km of ¡§on effort¡§ survey was conducted
while 100% of ¡§on effort¡¨
survey was conducted under favourable conditions (Beaufort Sea State 3 or
better). The details are shown
below:-
5.7.2 The effort summary and sightings data are
shown in Tables 5.3 and 5.4, respectively. The survey effort conducted in January 2013 are plotted in Figure 5a-c. For Table 5.3, only on-effort information
is included. Transects conducted in all Beaufort Sea State are included.
Compared to previous monthly reports, the whole number Beaufort Sea State scale
is used so as to ease comparison with other dolphin monitoring reports.
Table 5.3 Impact
Dolphin Monitoring Survey Effort Summary
|
Survey
|
Date
|
Status
|
Sea
State
(on
effort only)
|
Distance
(km)
|
|
1
|
08-01-13
|
ON
|
1
|
7.4
|
|
08-01-13
|
ON
|
2
|
49.1
|
|
08-01-13
|
ON
|
3
|
14.1
|
|
Total
|
70.6
|
|
09-01-13
|
ON
|
1
|
1.9
|
|
09-01-13
|
ON
|
2
|
38.7
|
|
Total
|
40.6
|
|
2
|
28-01-13
|
ON
|
1
|
16.9
|
|
28-01-13
|
ON
|
2
|
46.5
|
|
Total
|
63.4
|
|
29-01-13
|
ON
|
1
|
47.6
|
|
Total
|
47.6
|
|
TOTAL
January 2013
|
222.2
|
*Remark: Surveys conduct under Beaufort Sea State 3 or below are
considered as under favourable condition.
Table 5.4 Impact
Dolphin Monitoring Survey Details in January 2013
|
Date
|
Location
(transect line)
|
No. Sightings
¡§ON EFFORT¡¨
|
No. Sightings
¡§OPPORTUNISTIC¡¨
|
|
08-01-13
|
NW Lantau
(1-8,21,22)
|
3
|
0
|
|
09-01-13
|
NW & NE
Lantau (9-20,23)
|
1
|
0
|
|
28-01-13
|
NW Lantau (1-6)
|
8
|
3
|
|
29-01-13
|
NW & NE
Lantau (7-9,10-20,23)
|
0
|
0
|
|
Total in January 2013
|
12
|
3
|
5.7.3
A total
of fifteen dolphin sightings
were recorded during the two surveys, three on the 8 January 2013, one on the 9 January 2013 and eleven on the 28 January 2013.
Of the fifteen
sightings, twelve
were ¡§on effort¡¨ (which are all under favourable condition) and three were ¡§opportunistic¡¨. A total of forty-six individuals were sighted from the two impact
dolphin surveys in the reporting period. Sighting details are summarised and
plotted in Appendix K and Figure 5c, respectively.
5.7.4
Behaviour:
seven groups were feeding while none of them were associated with a fishing vessel; three groups were recorded as travelling; three groups were associated with multiple behaviour (feeding and surface active); one group was recorded as surface active; the behavior of
one group was unknown.
5.7.5
Noteworthy
Observations: two
mother and calf pairs were noted which
were considered
not the same.
5.7.6
Noteworthy
Observations: other non-project related marine works were observed in both NWL
and NEL areas, respectively; in particular in the vicinity of transect line 2, 4, 5, 11, 12 and 23.
5.7.7
The
event action plan is annexed in Appendix L.
6.1.1 Site Inspections were carried out on a
weekly basis to monitor the implementation of proper environmental pollution
control and mitigation measures for the Project. In the reporting month, 4 site inspections were carried out on 3, 10, 17, 24 and 31 January 2013.
6.1.2 Particular observations during the site
inspections are described below:
Air Quality
6.1.3 No adverse observation was identified in the
reporting month.
Noise
6.1.4 Air compressor was found not fitted with
valid noise emission label on barge FTB18. The Contractor was reminded to
ensure all air compressors on barge FTB18 are fitted with valid noise emission
labels. Air compressor was fitted with valid noise emission label on barge
FTB18 in the reporting month. (Closed)
Water Quality
6.1.5 Silt curtain installed for stone column
installation works on barge FTB18 was found damaged. The Contractor was
reminded to keep monitor and well maintain of the silt curtain more frequently to
ensure the silt curtain are fully functional. The damaged silt curtain found on
barge FTB18 was fixed in the reporting month. (Closed)
6.1.6 Defects were noticed at parts of the
perimeter silt curtain at portions E1 and C2c. The Contractor was reminded to
swiftly rectify the perimeter silt curtain in particular the portions where
defects were observed to ensure the sediment plume generated by construction
activities could be prevented from discharging to areas outside the site
boundary. (Follow up)
6.1.7 It was noticed that a localised silt curtain
was readily adjacent to Barge AP4 but was not deployed to enclose the active
stone column installation at Portion A. The Contractor was reminded to deploy
the localized silt curtain to enclose active stone column installation. (Follow
up)
Chemical and Waste Management
Waste
6.1.8 Water was observed dripping from the pipe
connected to the air conditioner. The Contractor provided mitigation measures
by placing a bucket to collect water that dripped from the air conditioner. (Closed)
6.1.9 Garbages accumulated on barge Kiu Chi was
observed. The Contractor was remineded to clear up the garbages frequently to
keep site tidy. Garbages accumulated on barge Kiu Chi was cleared in the
reporting month. (Closed)
6.1.10 Food waste was observed left outside of the
bin on barge SHB 402. The Contractor rectified the situation by putting the
food waste into the bin. The Contractor is reminded to keep the site at clean
and tidy condition. (Reminder)
6.1.11 Although the content of the stockpile on
barge Fu Tat was dampened, however, the Contractor was remineded to watering
the stockpile frequently to suppress fugitive dust generated. (Reminder)
6.1.12 Stagnant water accumulated inside the car tire on barge Sang Han Bo 205 and inside the
drip tray on barge Sang Han Bo 210 were observed. The Contractor was reminded
to clear the water or open a hole on the tire on Sang Han Bo 205 to prevent mosquito breeding and to clear the water
accumulated inside the drip tray on barge Sang Han Bo 210 respectively.
Stagnant water accumulated inside the wheel tire on barge Sang Han Bo 205 and
inside the drip tray on barge Sang Han Bo 210 were removed in the reporting
month. (Closed)
6.1.13 Oil drums were found improperly stored on
barge FTB16 and FTB19. The Contractor was reminded to provide drip tray to
prevent oil leakage. Oil drums were properly stored in trip tray on barge FTB16
and the oil drums stored on barge FTB19 were removed in the reporting
month. (Closed)
6.1.14 Oil stains were found underneath a pack of
cable and on the floor of barge Fai Yue 3228. The Contractor rectified the
situation by clearing the oil stain with absorption material and the absorption
material were disposed of as chemical waste. (Closed).
6.1.15 Oil was found accumulated inside the drip
tray on barge FTB20. The Contractor rectified the situation by
clearing the waste oil inside the drip tray, the Contractor is reminded to
dispose the waste oil as chemical waste. (reminder)
6.1.16 Uncovered open holes in the bundings and
drip trays were found on barge FTB18. The Contractor was reminded to seal/cover
the open holes properly to prevent oil leakage. Open holes in the bundings and
drip trays found on barge FTB18 were covered in the reporting month (Closed)
Landscape and Visual Impact
6.1.17 No relevant works was carried out in the
reporting month.
Others
6.1.18 No adverse observation was identified in the
reporting month.
6.1.19 The Contractor had rectified most of the
observations as identified during environmental site inspection in the
reporting month. Rectifications of remaining identified items are undergoing by
the Contractor. Follow-up inspections on the status on provision of mitigation
measures will be conducted to ensure all identified items are mitigated
properly.
6.2
Advice on the Solid and Liquid Waste
Management Status
6.2.1 The Contractor had registered as a chemical
waste producer for this Project. Receptacles were available for general refuse
collection and sorting.
6.2.2 As advised by the Contractor, 1,238.5 m3 of sand
fill, and 98,988.7 m3 of rock fill were imported
for the Project use in the reporting period. 1,400.0 L of chemical waste (liquid) were generated and disposed of in the
reporting period. 4.9
tonnes of general refuse were generated and disposed of in the reporting
period. Monthly summary of waste flow table is detailed in Appendix M.
6.2.3 The Contractor is advised to properly maintain on site
C&D materials and wastes storage, collection, sorting and recording system,
dispose of C&D materials and wastes at designated ground and maximize reuse
/ recycle of C&D materials and wastes. The Contractor is reminded to
properly maintain the site tidiness and dispose of the wastes accumulated on
site regularly and properly.
6.2.4 The Contractor is reminded that chemical
waste should be properly treated and stored temporarily in designated chemical
waste storage area on site in accordance with the Code of Practice on the
Packaging, Labeling and Storage of Chemical Wastes.
6.3
Environmental Licenses and Permits
6.3.1 The environmental licenses and permits for
the Project and valid in the reporting month is summarized in Table 6.1.
Table 6.1 Summary
of Environmental Licensing and Permit Status
|
Statutory Reference
|
License/ Permit
|
License or Permit No.
|
Valid Period
|
License/ Permit Holder
|
Remarks
|
|
From
|
To
|
|
EIAO
|
Environmental
Permit
|
EP-353/2009/E
|
16/10/2012
|
N/A
|
HyD
|
Hong Kong ¡V Zhuhai
¡V Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities
|
|
EP-354/2009/A
|
08/12/2010
|
N/A
|
Tuen Mun ¡V Chek
Lap Kok Link (TMCLKL Southern Landfall
Reclamation only)
|
|
APCO
|
NA notification
|
--
|
30/12/2011
|
--
|
CHEC
|
Works Area WA2 and
WA3
|
|
APCO
|
NA notification
|
--
|
17/01/2012
|
--
|
CHEC
|
Works Area WA4
|
|
WDO
|
Chemical Waste
Producer Registration
|
5213-951-C1186-21
|
30/3/2012
|
N/A
|
CHEC
|
Chemical waste produced
in Contract HY/2010/02
|
|
WDO
|
Chemical Waste
Producer Registration
|
5213-974-C3750-01
|
31/10/2012
|
--
|
CHEC
|
Registration as
Chemical Waste Producer at To Kau Wan(WA4)
|
|
WDO
|
Chemical Waste
Producer Registration
|
5213-839-C3750-02
|
13/09/2012
|
--
|
CHEC
|
Registration as
Chemical Waste Producer at TKO 137(FB)
|
|
WDO
|
Billing
Account for Disposal of
Construction Waste
|
7014181
|
05/12/2011
|
N/A
|
CHEC
|
Waste disposal in
Contract HY/2010/02
|
|
NCO
|
Construction
Noise Permit
|
GW-RS1111-12
|
01/11/2012
|
30/04/2013
|
CHEC
|
Works Area WA3 in Siu Ho Wan
|
|
NCO
|
Construction Noise
Permit
|
GW-RS0861-12
|
24/8/2012
|
23/2/2013
|
CHEC
|
Works Area WA2 in
Tung Chung
|
|
NCO
|
Construction Noise
Permit
|
GW-RS1360-12
|
21/12/2012
|
20/6/2013
(Renewal application in process)
|
CHEC
|
Marine-based areas
in Contract HY/2010/02
|
|
NCO
|
Construction Noise
Permit
|
N/A
|
Application in
process
|
N/A
|
CHEC
|
Works
Area WA 4 in
Contract HY/2010/02
|
6.4
Implementation Status of Environmental Mitigation
Measures
6.4.1 In response to the site audit findings, the
Contractors carried out corrective actions.
6.4.2 A summary of the Implementation Schedule of
Environmental Mitigation Measures (EMIS) is presented in Appendix C. Most of
the necessary mitigation measures were implemented properly.
6.4.3 Training of marine travel route for marine
vessels operator was given to relevant staff and relevant records were kept
properly.
6.4.4 Regarding the implementation of dolphin
monitoring and protection measures (i.e. implementation of Dolphin Watching
Plan, Dolphin Exclusion Zone and Silt Curtain integrity Check), regular
checking were conducted by the experienced MMOs within the works area to ensure
no dolphin was trapped by the enclosed silt curtain systems. Any dolphin spotted
within the enclosed silt curtain systems was reported and recorded. Relevant
procedures were followed and measures were well implemented. Silt curtain
systems were also inspected timely in accordance to the submitted plan. All
inspection records were kept properly.
6.4.5 As informed by the Contractor, insufficient
mitigation measures were noted during a joint site inspection with the
representative of the Contractor and the Resident Engineer in the after from
14:30 to 16:00 of 28 Jan 2013.
6.4.6 It was noticed that part of the demarcation
for Zone F was missing; being contrary to the other condition 3.d.16 of the
above CNP. In addition , Some generators and air compressors on barge FTB-16 in
Zone S4 were not completely screened by the acoustic baffles and parts of those
powered mechanical equipment (PME) were visible from Hong Kong SkyCity Marriott
Hotel (noise sensitive receiver); being contrary to other condition of the CNP.
It is understood that the set up of acoustic baffles for FTB-20 in Zone S5 was
identical to FTB-16 in Zone S4. Therefore the Contractor was advised to inspect and rectify (if necessary) the
acoustic baffles so as to comply with other condition 3.d.13 of the CNP.
6.4.7 In view of EPD¡¦s findings on 28 Jan 2013, the
Contractor is reminded not to operate those PME during restricted hours without
compliance with the CNP conditions. The Contractor was reminded to carry out necessary actions to rectify the
above deficiencies.
6.4.8 As informed by the Contractor on 9
February 2013, the deficiencies
were rectified. 7 nos. of demarcation (were no more visible) for Zone F have been re-deployed.
6.4.9 Extra noise barriers were installed onto barge FTB-16 in Zone S4 and
FTB-20 in S5. generators and air compressors on barge FTB-16 in Zone S4 and
FTB-20 in S5 were completely screened
by the acoustic baffles and parts of those powered mechanical equipment (PME)
were no more visible from Hong Kong SkyCity Marriott Hotel (noise sensitive
receiver).
6.4.10 The Contractor was reminded to strictly comply with the condition of the CNP.
6.4.11 Acoustic decoupling measures on noisy plants
on construction vessels were checked regularly and these measures were well
implemented.
6.5
Summary of Exceedances of the Environmental
Quality Performance Limit
6.5.1 No Action/Limit Level exceedance of 1-hour
TSP and 24-hour TSP results
was recorded in the reporting month.
6.5.2 For construction noise, no Action and Limit
Level exceedance was recorded at all monitoring stations in the reporting
period.
6.5.3 Six (6) Action Level exceedances were recorded at measured suspended solids
(SS) values (in mg/L) in
the reporting month. Investigation result show that the exceedances were not
due to the Project works.
6.5.4 Cumulative statistics on exceedance is
provided in Appendix N.
6.6
Summary of Complaints, Notification of
Summons and Successful Prosecutions
6.6.1 The Environmental Complaint Handling
Procedure is annexed in Figure 6.
6.6.2 EPD referred a complaint from a complainant on 18 Jan
2013 who advised that turbid
water and concrete/cement was arising from the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge
Hong Kong Projects to marine water. The source of turbid water and
concrete/cement was not specified by the complainant.
6.6.2.1 As informed by the Contractor (China Harbour
Engineering Company Ltd.), stone column construction was being
carried out on 14 -18 Jan 13 at the Portions B, D, C2a, C2c and E2 of the Hong
Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities (HKBCF) reclamation works (the location of
each Portion is shown in Figure 1 ¡V layout map of the HKBCF reclamation works).
Silt curtain integrity checking records of 14-18 Jan 13 show that defects were
found at parts of the perimeter silt curtain.
6.6.2.2 As informed by the Contractor, rectification
measures such as maintenance work of the silt curtain was carried out on a
daily basis from 14 to 31 Jan 13 (except 16, 20 and 27 Jan 13) and the
tentative date for completion of the maintenance of the silt curtain will be on
or before 21 Feb13.
6.6.2.3 As informed by the Contractor, preventive
actions such as daily inspection of silt curtain were carried out to review the
adequacy and effectiveness of the silt curtain and there were no incidents of onsite
leakage of turbid water and/or concrete/cement arising from project from 14
to18 Jan 13.
6.6.2.4 With reference to the available monitoring
records no silt plumes or turbid water were observed during impact water
quality monitoring on 14 ¡V 31 Jan 13. Moreover there were no exceedances of
turbidity level recorded in Jan 13. Although 5 results of depth averaged
measured Suspended Solids (SS) levels exceeded the action level, these
exceedances were not considered being caused by the project after investigation.
6.6.2.5 Therefore in accordance with the
abovementioned observations, it could not be concluded whether the complaint
was considered as project related or not. However the Contractor was reminded
to implement necessary mitigation measures.
6.6.2.6 Follow up site inspections were conducted on
24 and 31 Jan 13, please refer to ¡§Follow Up Site Visit¡¨ for details
of findings.
l Defect of
localised silt curtain was observed during the Site Inspection Audit conducted
on barge FTB-18 on 10 Jan 13. According to the photo record provided by the
Contractor, these defect
was rectified by the Contractor before the Site Inspection Audit conducted on 24 Jan 13.
l During the joint
site inspection with the representatives of the Contractor and Residential Engineer
on 31 Jan 13, it was noticed that a localised silt curtain was readily adjacent
to Barge AP4 but was not deployed to enclose the active stone column
installation at Portion A. However the Contractor rectified the situation by
providing the localised silt curtain to the active stone column installation on
the same day.
l Defects were
noticed at parts of the perimeter silt curtain at portions E1 and C2c. The
Contractor was reminded to swiftly rectify the perimeter silt curtain in particular
the portions where defects were observed to ensure the sediment plume generated
by construction activities could be prevented from discharging to areas outside
the site boundary.
6.6.2.7 The Contractor was reminded to implement
mitigation measures as stated below:
l The Contractor
was reminded to carry out regular
inspection of the deployed silt
curtains to review the
integrity and effectiveness of the perimeter silt curtains deployed at the
boundary of HKBCF and the localised silt curtain deployed during
active stone column installation.
l
The
Contractor was reminded to swiftly rectify the perimeter silt curtain in particular the portions which defects were
observed to ensure the sediment
plume generated by construction activities could
be prevented from discharging to areas outside the site boundary.
l The Contractor
was reminded to reinforce the provision of localised silt curtain to all stone
column vessels to ensure the sediment plume generated by construction
activities could be prevented from discharging to areas outside the site
boundary.
6.6.3 No notification of summons and prosecution
was received in the reporting period.
6.6.4 Statistics on complaints, notifications of
summons and successful prosecutions are summarized in Appendix N.
7
FUTURE KEY ISSUES
7.1.1 As informed by the Contractor, the major
works for the Project in February and March 2013 will be:-
Marine-based Works
-
Marine-base
-
Cellular
structure installation
-
Laying
geo-textile
-
Sand
blanket trial
-
Maintenance
of Silt curtain
-
Stone
column installation
-
Band
drain installation
-
Backfill
cellular structure
-
Stone
blanket laying
Land-based Works
-
Maintenance
works of Site Office at Works Area WA2
-
Maintenance
works of Public Works Regional Laboratory at Works Area WA3
-
Geo-textile
fabrication at Works Area WA2
-
Stone
column installation barges setup and their maintenance works at Works Area WA4
-
Silt
curtain fabrication at Works Area WA4
7.2
Key Issues for the Coming Month
7.2.1 Key issues to be considered in the coming
months:-
- Site runoff should be
properly collected and treated prior to discharge;
- Minimize loss of sediment
from filling works;
- Regular review and
maintenance of silt curtain systems, drainage systems and desilting facilities;
- Exposed surfaces/soil stockpiles
should be properly treated to avoid generation of silty surface run-off during
rainstorm;
- Regular review and
maintenance of wheel washing facilities provided at all site entrances/exits;
- Conduct regular inspection
of various working machineries and vessels within works areas to avoid any dark
smoke emission;
- Suppress dust generated
from work processes with use of bagged cements, earth movements, excavation
activities, exposed surfaces/soil stockpiles and haul road traffic;
- Quieter powered mechanical
equipment should be used;
- Provision of proper and
effective noise control measures for operating equipment and machinery on-site,
such as erection of movable noise barriers or enclosure for noisy plants;
- Closely check and replace
the sound insulation materials regularly;
- Better scheduling of
construction works to minimize noise nuisance;
- Properly store and label
oil drums and chemical containers placed on site;
- Proper chemicals, chemical
wastes and wastes management;
- Maintenance works should be
carried out within roofed, paved and confined areas;
- Collection and segregation
of construction waste and general refuse on land and in the sea should be
carried out properly and regularly;
and
- Proper protection and
regular inspection of existing trees, transplanted/retained trees.
7.3
Monitoring Schedule for the Coming Month
7.3.1
The tentative schedule for environmental
monitoring in January 2013 is provided in Appendix F.
8.1.1 The construction phase and EM&A
programme of the Project commenced on 12 March 2012.
8.1.2 All 1-hour TSP and 24-hour TSP results were below the Action
and Limit Level at all monitoring locations in the reporting month.
8.1.3 For construction noise, no Action and Limit
Level exceedance was recorded at all monitoring stations in the reporting
period. Investigation result show that the exceedances were not due to the
Project works.
8.1.4 Six (6) Action Level exceedances were recorded at measured suspended solids (SS) values (in mg/L) in the
reporting month. Investigation results show that the exceedances were not due to the Project works.
8.1.5 A total of fifteen dolphin sightings were recorded during the two surveys, three on the 8 January 2013, one on the 9 January 2013 and eleven on the 28 January 2013. Of the fifteen sightings, twelve were ¡§on effort¡¨ (which are all under favourable condition) and three were ¡§opportunistic¡¨. A total of forty-six individuals were sighted from the two
impact dolphin surveys in the reporting period. Sighting details are summarised
and plotted in Appendix K and Figure 5c, respectively.
8.1.6 Behaviour: seven groups were feeding while none of them were associated with a
fishing vessel; three
groups were recorded as
travelling; three groups were associated
with multiple behaviour (feeding and surface active); one group was recorded as surface active; the behavior of one group was unknown.
8.1.7 Environmental site inspection was carried
out 5 times in January 2013. Recommendations on remedial actions were given to the Contractors for
the deficiencies identified during the site audits.
6.6.2.8 As informed
by the EPD on 18 January 2013, one complaint was received on 18
January 2013. In
accordance with the investigation findings, it could not be concluded whether the
complaint was considered as project related or not. However the Contractor was
reminded to implement necessary mitigation measures.
8.1.8
No notification of summons and prosecution was received
in the reporting period.
8.2
Recommendations
8.2.1 According to the environmental site
inspections performed in the reporting month, the following recommendations
were provided:
Air Quality Impact
l All working
plants and vessels on site should be regularly inspected and properly
maintained to avoid dark smoke emission.
l All vehicles should be washed to remove any
dusty materials before leaving the site.
l Haul roads should be sufficiently dampened
to minimize fugitive dust generation.
l Wheel washing facilities should be properly
maintained and reviewed to ensure properly functioning.
l Temporary exposed slopes and open stockpiles
should be properly covered.
l Enclosure should be erected for cement
debagging, batching and mixing operations.
l Water spraying should be provided to suppress fugitive
dust for any dusty construction activity.
Construction Noise Impact
l Quieter powered
mechanical equipment should be used as far as possible.
l Noisy operations
should be oriented to a direction away from sensitive receivers as far as
possible.
l Proper and
effective noise control measures for operating equipment and machinery on-site
should be provided, such as erection of movable noise barriers or enclosure for
noisy plants. Closely check and replace the sound insulation materials
regularly
l Vessels and
equipment operating should be checked regularly and properly maintained.
l Noise Emission
Label (NEL) shall be affixed to the air compressor and hand-held breaker
operating within works area.
l Better scheduling
of construction works to minimize noise nuisance.
Water Quality Impact
l Regular review
and maintenance of silt curtain systems, drainage systems and desilting
facilities in order to make sure they are functioning effectively.
l Construction of
seawall should be completed as early as possible.
l Regular inspect
and review the loading process from barges to avoid splashing of material.
l Silt, debris and
leaves accumulated at public drains, wheel washing bays and perimeter
u-channels and desilting facilities should be cleaned up regularly.
l Silty effluent
should be treated/ desilted before discharged. Untreated effluent should be
prevented from entering public drain channel.
l Proper drainage
channels/bunds should be provided at the site boundaries to collect/intercept
the surface run-off from works areas.
l Exposed slopes
and stockpiles should be covered up properly during rainstorm.
Chemical and Waste Management
l All types of
wastes, both on land and floating in the sea, should be collected and sorted
properly and disposed of timely and properly. They should be properly stored in
designated areas within works areas temporarily.
l All chemical
containers, batteries and oil drums should be properly stored and labelled.
l All plants and
vehicles on site should be properly maintained to prevent oil leakage. Proper measures, like drip trays and/or bundings, should be provided for
retaining leaked oil/chemical from plants.
l All kinds of
maintenance works should be carried out within roofed, paved and confined
areas.
l All drain holes
of the drip trays utilized within works areas should be properly plugged to
avoid any oil and chemical waste leakage.
l Oil stains on
soil surface, accumulated oil mixture and empty chemical containers should be
cleared and disposed of as chemical waste.
l Regular review should be conducted for working barges and patrol boats
to ensure sufficient measures and spill control kits were provided on working
barges and patrol boats to avoid any spreading of leaked oil/chemicals.
Landscape and Visual Impact
l All existing,
retained/transplanted trees at the works areas should be properly fenced off
and regularly inspected.